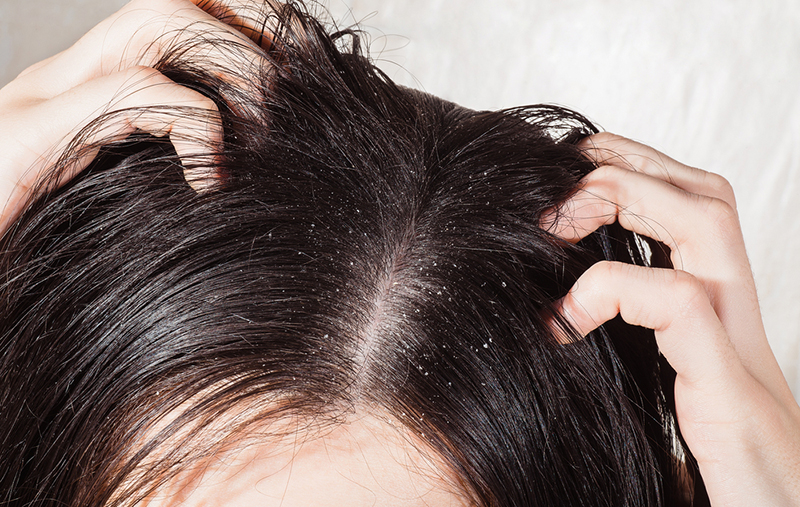
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, recurrent, inflammatory disease. It manifests as areas of redness and flaking on the scalp, face and body.
Seborrheic dermatitis occurs more frequently in men in adolescence and at age 19-20, with women less frequently. Sometimes it occurs in infants in the first weeks of life, but disappears on its own by 7-9 months.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis are complex
Most often it is a combination of several factors:
How seborrheic dermatitis develops
The combination of unfavorable factors changes the pH balance of the skin to the alkaline side. The composition of sebum is disturbed and the fungus is activated on the skin, grows intensively and results in an inflammatory reaction, skin flaking and sometimes the addition of a secondary infection.
The mild form causes only scalp flaking. In more severe cases, spots of pale pink and bright pink appear on the skin, covered with yellow scales. Itching and severe dandruff are bothersome. The spots may converge and move to the forehead and behind-the-ear folds. As the disease progresses, rashes may appear on the face and back. Hair either becomes dry and brittle, or greasy and sticky, and also falls out heavily.
The chronic course of the disease and discomfort from it often lead to a deterioration of the psycho-emotional state. It reduces a person's social activity and quality of life.
How it is treated during exacerbation and remission phases
Antifungal shampoos are prescribed as a way to suppress the activity of Malassezia fungus. It is necessary to use them permanently in the acute stage.
To maintain remission, they are used less frequently and in lower concentrations, and peels and scrubs are prescribed instead.
Hardware treatment methods are successfully used. Such as gas-liquid peels, darsonval and laser therapy, which clean the scalp from scales and reduce sebum production.
Botulinum toxin is also under investigation as a treatment for seborrheic dermatitis. Botulinum toxin slows down the sebaceous and sweat glands by reducing sebum and sweat production, thus inhibiting the reproduction of fungus on the scalp.
Plasma therapy of the scalp has a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect, which is necessary for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, it reduces the dryness of the scalp and regulates sebum production, while stimulating hair growth and improving its quality.
Recommendations for remission
With timely visit to the doctor seborrheic dermatitis successfully passes into remission and may not bother for a long time. You will forget about dandruff, excessive greasiness and itchy scalp if you follow some simple recommendations:
You can find shampoos, peels and other treatments for free in our IHairium app. Professional recommendations for restoration.
Seborrheic dermatitis occurs more frequently in men in adolescence and at age 19-20, with women less frequently. Sometimes it occurs in infants in the first weeks of life, but disappears on its own by 7-9 months.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis are complex
Most often it is a combination of several factors:
- The conditionally pathogenic fungus Malassezia. Normally it is found on the scalp and on the body, but when greasiness is increased, it becomes active and causes inflammation;
- Changes in the quality and quantity of sebum. It is a genetic predisposition of sebaceous gland secretion and disruption of the epidermal barrier;
- Hormonal imbalance. It occurs with an increase in male sex hormones, during menopause, pregnancy, etc;
- Psycho-emotional stress. Stresses lead to increased production of sebum and sweat;
- Decreased immunity. In the presence of viral, immunodeficiency, cancer and HIV infections;
- Taking antibacterial drugs. Some antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs disrupt the microflora of the scalp and may become triggering agents;
- Improper home care. Frequent use of sulfate-free and dry shampoos, aggressive and low-quality products and washing the head less frequently than 2-3 times a week.
How seborrheic dermatitis develops
The combination of unfavorable factors changes the pH balance of the skin to the alkaline side. The composition of sebum is disturbed and the fungus is activated on the skin, grows intensively and results in an inflammatory reaction, skin flaking and sometimes the addition of a secondary infection.
The mild form causes only scalp flaking. In more severe cases, spots of pale pink and bright pink appear on the skin, covered with yellow scales. Itching and severe dandruff are bothersome. The spots may converge and move to the forehead and behind-the-ear folds. As the disease progresses, rashes may appear on the face and back. Hair either becomes dry and brittle, or greasy and sticky, and also falls out heavily.
The chronic course of the disease and discomfort from it often lead to a deterioration of the psycho-emotional state. It reduces a person's social activity and quality of life.
How it is treated during exacerbation and remission phases
Antifungal shampoos are prescribed as a way to suppress the activity of Malassezia fungus. It is necessary to use them permanently in the acute stage.
To maintain remission, they are used less frequently and in lower concentrations, and peels and scrubs are prescribed instead.
Hardware treatment methods are successfully used. Such as gas-liquid peels, darsonval and laser therapy, which clean the scalp from scales and reduce sebum production.
Botulinum toxin is also under investigation as a treatment for seborrheic dermatitis. Botulinum toxin slows down the sebaceous and sweat glands by reducing sebum and sweat production, thus inhibiting the reproduction of fungus on the scalp.
Plasma therapy of the scalp has a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect, which is necessary for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, it reduces the dryness of the scalp and regulates sebum production, while stimulating hair growth and improving its quality.
Recommendations for remission
With timely visit to the doctor seborrheic dermatitis successfully passes into remission and may not bother for a long time. You will forget about dandruff, excessive greasiness and itchy scalp if you follow some simple recommendations:
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle (quitting smoking and alcohol, limiting sweets, spicy and carbonated foods);
- Reduce the amount of stress;
- Get enough sleep, and do daily physical activity;
- Use therapeutic shampoos and peels, selected by a trichologist to maintain remission.
You can find shampoos, peels and other treatments for free in our IHairium app. Professional recommendations for restoration.