Alopecia areata: causes, symptoms and treatments
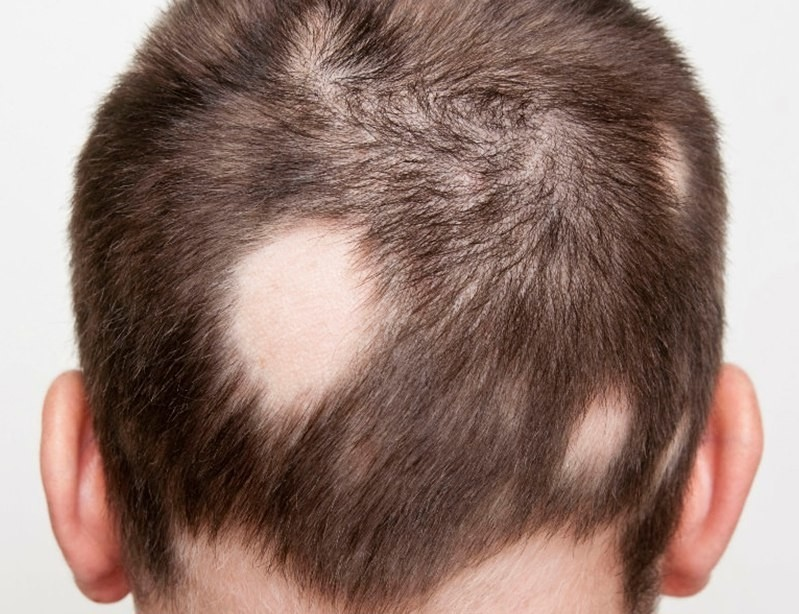
Alopecia areata is a form of alopecia characterized by the formation of round or oval areas of baldness on the scalp. This is a fairly common disease that can have a serious impact on the psychological state of the patient.
The causes of alopecia areata are not fully understood, but studies show that it may be due to a compromised immune system. Sudden changes in the immune response can attack one's own hair follicles and cause areas of baldness to form. Genetic predisposition may also play a role in the development of alopecia areata.
Symptoms of alopecia areata can vary, but the most common is the formation of round or oval areas of baldness on the scalp. These areas of baldness can vary in size and tend to gradually merge with each other. In some cases, the skin around areas of baldness may be inflamed or itchy.
Diagnosis of alopecia areata requires a professional approach. The most common causes of alopecia areata are considered to be diseases of the endocrine system (thyroid gland, adrenal glands, hypothalamus and pituitary gland), stress, decreased immunity and iron deficiency anemia.
A trichologist performs a thorough physical examination of the scalp and hair, and collects information about the patient's medical and family history. Additional tests, such as a skin biopsy or blood tests, may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for alopecia areata depends on the cause and individual characteristics of the patient. In some cases, baldness can happen on its own without medical intervention. However, if it affects the psychological state of the patient or the baldness continues, various treatments may be prescribed.
One of the main treatments for alopecia areata is the use of topical drugs such as minoxidil. This drug promotes hair growth and may help regenerate hair follicles. Corticosteroid medications may also be used to reduce inflammation and stimulate hair growth in areas of baldness.
In some cases, immunomodulators may be prescribed to suppress the autoimmune response and restore normal immune system function. These drugs require a doctor's prescription and health monitoring.
In addition to medical treatments, psychological support is also an important part of the healing process. Seeing a psychologist or engaging in practices such as yoga or meditation can help manage the stress associated with alopecia areata.
It is important to understand that each case of alopecia areata is individual, and the results of treatment, as well as its duration, may vary depending on many factors. Therefore, it is recommended to contact professionals for individual advice and development of a treatment plan.
Alopecia areata is a form of alopecia characterized by the formation of round or oval areas of baldness on the scalp. This is a fairly common disease that can have a serious impact on the psychological state of the patient.
The causes of alopecia areata are not fully understood, but studies show that it may be due to a compromised immune system. Sudden changes in the immune response can attack one's own hair follicles and cause areas of baldness to form. Genetic predisposition may also play a role in the development of alopecia areata.
Symptoms of alopecia areata can vary, but the most common is the formation of round or oval areas of baldness on the scalp. These areas of baldness can vary in size and tend to gradually merge with each other. In some cases, the skin around areas of baldness may be inflamed or itchy.
Diagnosis of alopecia areata requires a professional approach. The most common causes of alopecia areata are considered to be diseases of the endocrine system (thyroid gland, adrenal glands, hypothalamus and pituitary gland), stress, decreased immunity and iron deficiency anemia.
A trichologist performs a thorough physical examination of the scalp and hair, and collects information about the patient's medical and family history. Additional tests, such as a skin biopsy or blood tests, may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for alopecia areata depends on the cause and individual characteristics of the patient. In some cases, baldness can happen on its own without medical intervention. However, if it affects the psychological state of the patient or the baldness continues, various treatments may be prescribed.
One of the main treatments for alopecia areata is the use of topical drugs such as minoxidil. This drug promotes hair growth and may help regenerate hair follicles. Corticosteroid medications may also be used to reduce inflammation and stimulate hair growth in areas of baldness.
In some cases, immunomodulators may be prescribed to suppress the autoimmune response and restore normal immune system function. These drugs require a doctor's prescription and health monitoring.
In addition to medical treatments, psychological support is also an important part of the healing process. Seeing a psychologist or engaging in practices such as yoga or meditation can help manage the stress associated with alopecia areata.
It is important to understand that each case of alopecia areata is individual, and the results of treatment, as well as its duration, may vary depending on many factors. Therefore, it is recommended to contact professionals for individual advice and development of a treatment plan.