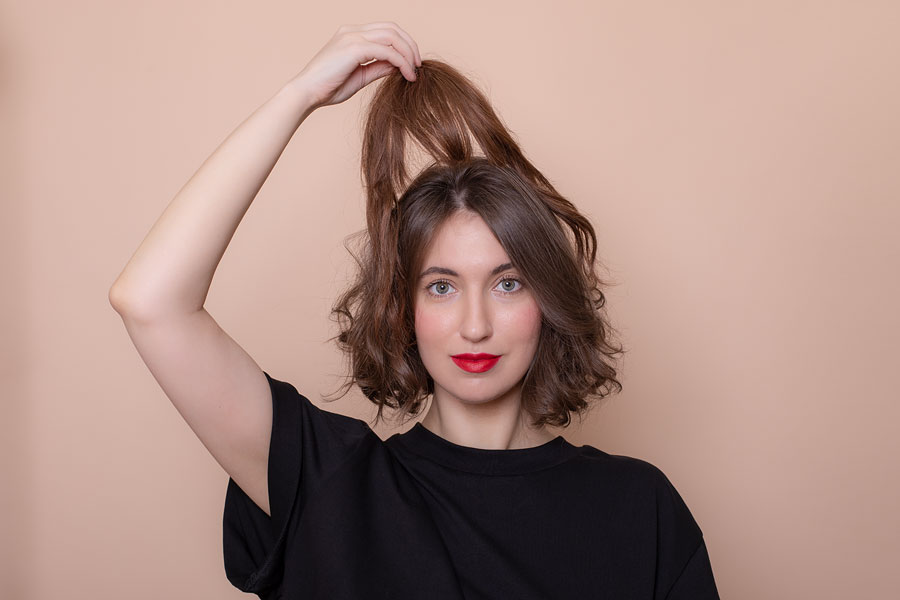
The pain in hair roots is a common condition experienced by many individuals. Trichodynia is a pathological condition and a symptom of various trichology problems where unpleasant sensations such as pain, burning, and tightness occur upon touching the hair-covered part of the head. Trichodynia can affect the entire head or be localized, occurring specifically upon touching the hair.
One of the most common reasons for hair root pain is excessive and frequent hair tension. This can be caused by tight hairstyles such as braids, ponytails, or improperly chosen accessories. Excessive tension on the hair leads to skin trauma on the scalp and inflammation.
Another cause of pain in hair roots is skin conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, folliculitis, and psoriasis. These conditions involve inflammation of the skin and can result in painful sensations in the hair root area. If there is suspicion of such conditions, it is necessary to consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Some scientists note a connection between trichodynia and diffuse hair loss, autoimmune conditions, and deficiency states (vitamins D, B12, and E, iron, zinc, etc.).
Another interesting theory about the origin of trichodynia is related to the release of substance P, responsible for transmitting pain impulses in the area of hair follicles, and the formation of inflammation around the hair follicle.
Finally, stress and emotional tension, particularly depression, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and increased anxiety, can also cause pain in hair roots. Severe stress affects various physiological processes in the body, including blood circulation in the scalp, leading to unpleasant sensations and hair root pain.
To alleviate or reduce the feeling of pain, scalp massage with fingertips, without pressing the hair against the scalp, proper scalp care, and alternating hairstyles with loose hair can be helpful. Managing stress through regular physical exercise, meditation, or other relaxation methods can also help reduce painful sensations.
It is important to remember that the cause of hair root pain may vary for each individual, and sometimes consultations with a doctor or hair specialist may be necessary to determine the exact cause and prescribe appropriate treatment.
One of the most common reasons for hair root pain is excessive and frequent hair tension. This can be caused by tight hairstyles such as braids, ponytails, or improperly chosen accessories. Excessive tension on the hair leads to skin trauma on the scalp and inflammation.
Another cause of pain in hair roots is skin conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, folliculitis, and psoriasis. These conditions involve inflammation of the skin and can result in painful sensations in the hair root area. If there is suspicion of such conditions, it is necessary to consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Some scientists note a connection between trichodynia and diffuse hair loss, autoimmune conditions, and deficiency states (vitamins D, B12, and E, iron, zinc, etc.).
Another interesting theory about the origin of trichodynia is related to the release of substance P, responsible for transmitting pain impulses in the area of hair follicles, and the formation of inflammation around the hair follicle.
Finally, stress and emotional tension, particularly depression, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and increased anxiety, can also cause pain in hair roots. Severe stress affects various physiological processes in the body, including blood circulation in the scalp, leading to unpleasant sensations and hair root pain.
To alleviate or reduce the feeling of pain, scalp massage with fingertips, without pressing the hair against the scalp, proper scalp care, and alternating hairstyles with loose hair can be helpful. Managing stress through regular physical exercise, meditation, or other relaxation methods can also help reduce painful sensations.
It is important to remember that the cause of hair root pain may vary for each individual, and sometimes consultations with a doctor or hair specialist may be necessary to determine the exact cause and prescribe appropriate treatment.